Home
Inagaki Laboratory conducts research into advanced mobility systems, including new mobility mechanisms and infrastructure. Specifically, we are developing uneven terrain walking control and motion planning for actual robots, with the ultimate goal of creating practical multi-legged robots. We are also studying energy management systems for buildings and communities that utilize the on-board storage batteries of electric and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (EVs and PHVs).
Multi-legged robot
Multilegged robots, which consist of six or more legs, are expected to be used in various environments because of their excellent ability to traverse uneven terrain, high stability, and ability to carry heavy objects. Inagaki Laboratory researches and develops basic technologies such as gait control technology, motion planning methods, embedded systems, and sensor systems.
Since 2021, a joint research project on a large-sized hexapod robot (SOL) has been conducted among Shinmei Industry Co., Ltd., Nagoya University, and Nanzan University. This joint research has been adopted as a "Joint Research Promotion Program" of Aichi Science & Technology Foundation.
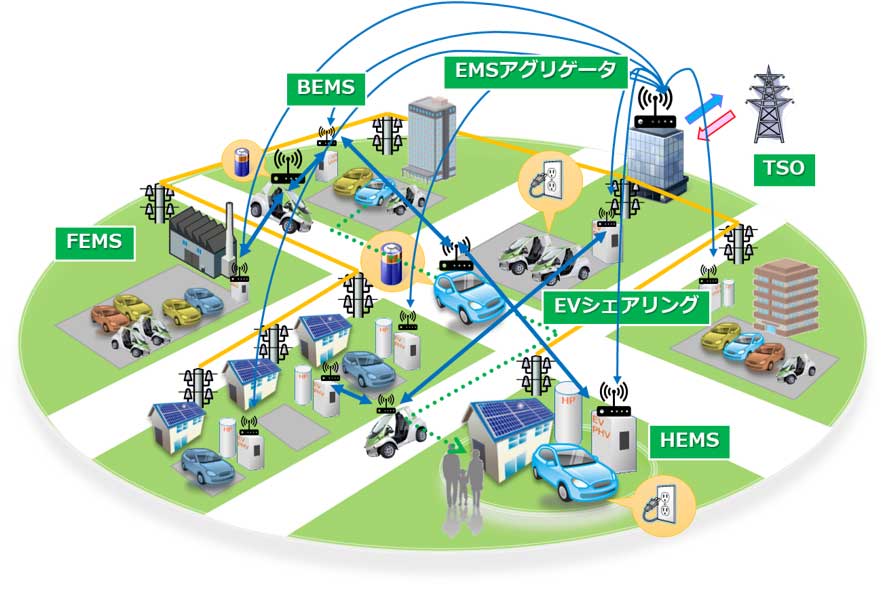
Energy Management System
By utilizing the batteries of electric vehicles (EVs) and plug-in hybrid vehicles (PHVs), it is expected that electricity in homes, buildings, and cities can be managed efficiently. Inagaki Laboratory is conducting research and development on fundamental technologies such as vehicle usage prediction, charging and discharging planning methods, and energy management system design.