Energy management system
駐車中にも車載蓄電池を活用する
電気自動車(EV)やプラグインハイブリッド車(PHV)には大容量の蓄電池が搭載されています.駐車中は次の走行に向けて充電をしますが,逆に電力に余裕があるときは放電して建物内の家電機器の電力消費に当てることができます.賢く車載蓄電池の充電と放電(充放電)を制御することにより,建物のエネルギー(電力)を賢く制御することができます.エネルギー管理システム(Energy management system: EMS)にとって,EVやPHVは有望なエネルギーバッファとなるのです.
稲垣研究室では,「1. 観測」「2. 予測」「3. 計画」を繰り返して車載蓄電池の充放電を制御する,モデル予測型EMSを研究しています.
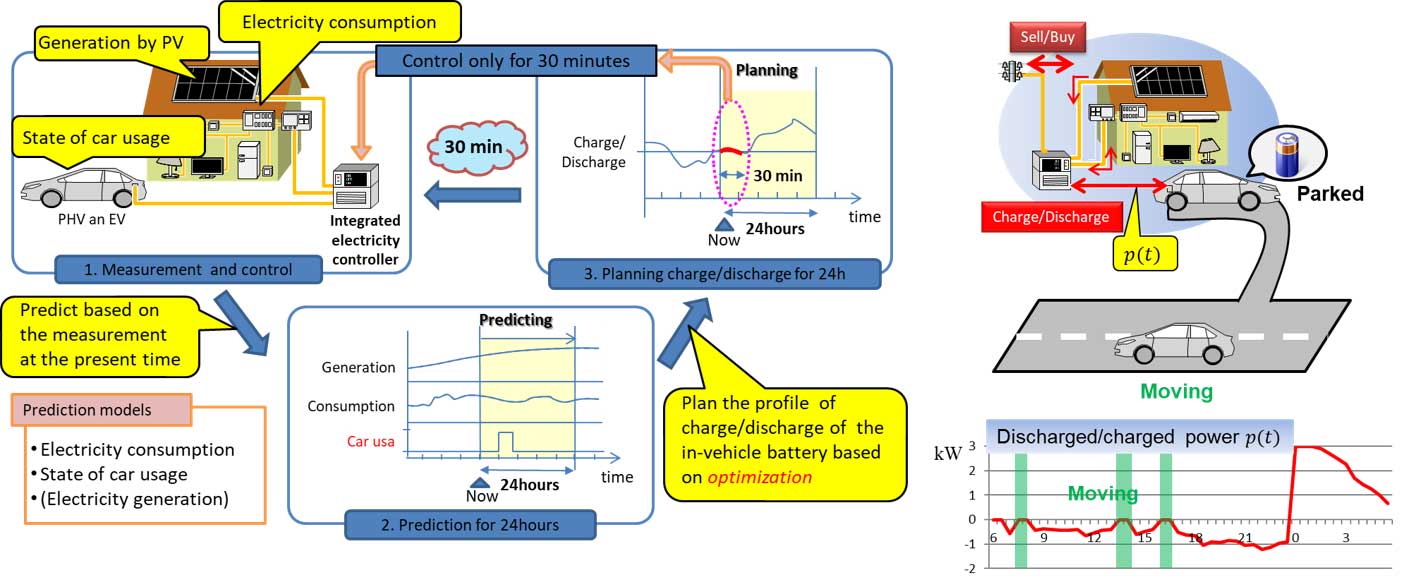
モデル予測型EMSの流れ:1. 現在の消費・発電電力,車の使用状況を観測し,2. 予測モデルを使ってそれらを24時間先まで予測,3. 予測したパターンを使って電気代が最小になるように24時間先までの充放電量を最適化計算する.そして,計画にしたがって充放電を制御し30分経ったら,また1. 観測から繰り返す.これにより,状況の変化に適応するEMSを実現することができる.
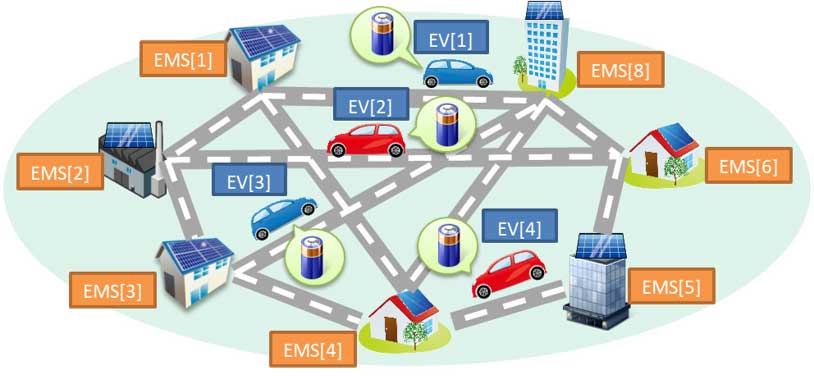
建物から地域全体へ
EVやPHVは移動する大型蓄電池とも言えます.街を移動するEVやPHVの車載蓄電池を統合的に管理して,地域全体のエネルギー管理を行う研究も進めています.車載蓄電池を統合的に管理するには,建物のEMS間で協調して充放電を制御する必要があります.本研究では,EMS間の協調を含めたモデル予測型EMSを開発すると共に,またEV・PHVと建物との間でやりとりされる電力の電気代の自動算出方法も開発しています.